编译原理complier
不可视境界线最后变动于:2023年4月11日 上午
COMPLIER-CS143
这篇文章所用到的代码结构其实复杂了一些, 看到个其他的解法
0. 预备知识
COOL语言
- 只能说是比较复杂, manuals和源码分析详见相关文档
- 比较典型的是继承树结构
1 | |
编译原理
- 词法分析->语法分析->语义分析
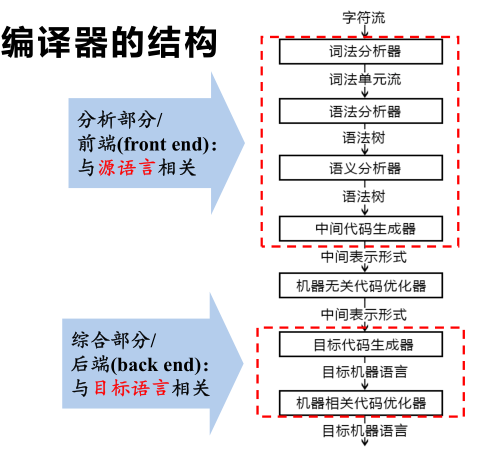
- 词法分析
- 从左向右逐行扫描源程序的字符,识别出各个单词,确定单词的类型。将识别出的单词转换成统一的机内表示——词法单元(token)形式
- 语法分析
- 语法分析器(parser)从词法分析器输出的token序列中识别出各类短语,并构造语法分析树(parse tree)
- 语义分析
- 收集标识符的属性信息&&语义检查
- 中间代码
- 三地址码 (Three-address Code)
三地址码由类似于汇编语言的指令序列组成,每个指令最多有三个操作数(operand) - 语法结构树/语法树 (Syntax Trees)
- 三地址码 (Three-address Code)
CS143实验文件结构
list.h:
- 注意到head是这个节点存储的数据, 而tail指向下一个节点, 构造节点时在这一串链表的头部添加新的节点.
1 | |
tree.h+cool-tree.h:
- All APS nodes are derived from tree_node.
- Lists of APS objects are implemented by the “list_node” template.
- Class_, Feature, Expression等等都是指向constructor(第二层)的指针. 前者是因为Class是c++关键字, 所以加上一个下划线.
- 属实很抽象, 我觉得三层结构的原因是为了把第二层作成一个通用class, 因为全是**纯虚**函数. 就像Feature那样. 确实是这样, 在把class method加入env的method_table中时只要给出Features指针(
typedef Feature_class* Feature)然后调用feature_add函数即可分配到method或者attr的add函数, 整了一个多态.
classDiagram
class tree_node{
int line_number
tree_node()
virtual tree_node *copy() = 0
virtual void dump(ostream& stream, int n) = 0
int get_line_number()
tree_node *set(tree_node *)
}
class list_node{
实现了三个
返回下标的迭代器
}
class node相关{
append_node
nil_node
single_list_node
}
tree_node --|> list_node
list_node --|> node相关
class Class__class{
virtual__get_name()
virtual__get_parent()
virtual__get_features()
virtual__get_filename()
virtual__dump_with_types(ostream&,int)
}
Class__class : define simple_phylum_Class_
class class__class{
Symbol name;
Symbol parent;
Features features;
Symbol filename;
}
Class__class --|> class__class
tree_node --|> Class__class
tree_node --|> Feature_class
class Feature_class{
全为纯虚函数:
dump_with_types(ostream&,int) = 0
Symbol get_name()
tc(EnvironmentP)
add_to_table(EnvironmentP)
}
class method_class{
Symbol name;
Formals formals;
Symbol return_type;
Expression expr;
get_return_type()
get_formals()
...
}
class attr_class{
Symbol name;
Symbol type_decl;
Expression init;
}
Feature_class --|> method_class
Feature_class --|> attr_class
tree_node --|> Formal_class
tree_node --|> Case_class
tree_node --|> Expression_class
stringtable:
- Symbol是指向Entry的指针
typedef Entry* Symbol;
classDiagram
direction RL
class Entry{
char *str;
int len;
int index;
}
Entry --|> StringEntry
Entry --|> IntEntry
Entry --|> IdEntry
class StringTable~Elem~{
List~Elem~ *tbl;
int index;
}
StringTable .. Entry
1. lexer - 词法分析
- 这一实验看上去就是逐字分析然后根据flex的语法返回token就完事了, 但要知道的是flex的内部原理仍然是有穷自动机finite automate, 具体概念可以看看课程PDF, flex的代码分析可见 这里, 肖哥的分析在 这里
- 字符串用到了stringtable. 具体见cool文档: We provide you with a string table implementation, which is discussed in detail in A Tour of the Cool
Support Code and in documentation in the code. For the moment, you only need to know that the type of string table entries is Symbol.
flex document
yylex()是扫描例程.- Actions中
yyless()andyymore()可以把yytext的字符放到或者取出自input stream中. #define yylval cool_yylval: 返回semantic value.- Start conditions: 这个就是匹配成对注释符的条件.
<QUOTE_COMMENT>"*)" { ... }%x QUOTE_COMMENT: exclusive声明. If it is exclusive, then only rules qualified with the start condition will be active.BEGIN(INITIAL);: `BEGIN(0/INITIAL)’ returns to the original state where only the rules with no start conditions are active.
文件:
- lexertest.cc是main函数所在文件, 我们写完cool.flex后flex使用此文件和众多依赖文件编译成lexer(executable)
- 开头一个handle_flags函数处理命令行参数. 具体见文件.
- 调用cool_yylex来每次得到一个token, 然后dump打印出来.
- cool-lex.cc即为flex自动生成的词法扫描自动机
- include中的cool-parser.h是一些宏定义, 比如token type.
2.parser - 语法分析
- 此阶段主要任务是构建AST树
- 文件关系:
- parser-phase.cc是main函数所在文件, 调用cool_yyparse函数
- 把词法分析编译出的lexer文件放进此PA的文件夹中完成词法分析
- cool.y为我们要编写的bison文件, cool-parse.cc为bison自动生成的源文件, parser为可执行文件
assignments/PA3/cool-tree.handcode.h: 这个真是手写的, 定义了每个class中extra的部分, 使用宏来支持自定义, 在之后的assignment中会加入更多的东西.
- If no parent is specified, the class inherits from the Object class.
make相关
- 这make文件中还出现了
ln -s命令, 居然只是用来将src或者include文件夹中的源文件复制到当前文件夹下, 真的是有点意义不明. .d文件doc : 为了不用手动更改一个.cc文件的header file prerequisites, 可以先通过编译器自动生成该文件的依赖, 把.d文件名也放到target部分, 输出到.d文件中, 再使用-include加入到makefile中.-include filenames…: This acts likeincludein every way except that there is no error (not even a warning) if any of the filenames (or any prerequisites of any of the filenames) do not exist or cannot be remade.
1 | |
bison:
bison所使用的是自底向上,左递归的分析方式。在语法分析这个过程中,可以过滤出一些不符合语法的错误,例如token排列不符合条件,无法规约。
在这种情况下必须进行错误处理程序,将token弹出栈(或者其他操作)。一个简单的例子
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22%union {
...
Class_ class_;
}
%type <class_> class
/* If no parent is specified, the class inherits from the Object class. */
/* 定义:以下token规约后的符号名称为"class" */
class :
/* 若当前栈中的token满足下面这条式子 */
CLASS TYPEID '{' dummy_feature_list '}' ';' /* ' */
/* 进行规约。在规约的同时执行以下这条式子 */
/* 注意,赋给$$的值,就是规约后新生成"class"的值 */
{ $$ = class_($2,idtable.add_string("Object"), $4, stringtable.add_string(curr_filename)); }
| /* 或者,如果满足以下式子 */
CLASS TYPEID INHERITS TYPEID '{' dummy_feature_list '}' ';'
{ $$ = class_($2,$4,$6,stringtable.add_string(curr_filename)); }
| /* 或者,如果捕获到了错误 */
error ';'
{}
;
语法点
You must declare bison “types” for your non-terminals and terminals that have attributes.
%type <program> programThis declaration says that the non-terminal program has type<program>. The use of the word “type” is misleading here; what it really means is that the attribute for the non-terminal program is stored in the program member of the union declaration in cool.y, which has type Program. By specifying the type%type <member_name> X Y Z ...
you instruct bison that the attributes of non-terminals (or terminals) X, Y, and Z have a type appropriate for the member member name of the union.All the union members and their types have similar names by design. It is a coincidence in the example above that the non-terminal program has the same name as a union member.
APS: 在cool_tour.pdf里
- The Cool abstract syntax is specified in a language called APS
- Phyla are really just types. That is, instead of having one large group of undifferentiated constructors, the constructors are grouped together according to function, 这个意思应该根据功能.
- the various kinds of abstract syntax tree nodes (let, +, etc.) are called constructors.
- Each constructor takes typed arguments and returns a typed result. The types may either be phyla or any ordinary C++ type.
- In fact, the phyla declarations are themselves compiled into C++ class declarations by an APS compiler.
- 我没搞清楚aps在哪里被用到了, 还有什么是aps compiler. 不会是自创的吧. 我居然找到一个aps2c++. 可惜没有什么注释可看.
- 重大发现 : bin文件夹下有个aps2c++, 可以将aps文件转化为
cool-tree.cc和cool-tree.h文件, 其中的class成员函数都有. 应该是默认生成的. 果然是自创的吧. 在初始文件中已经转化过了, 所以也不用太在意.- 在aps文件中定义的constructor在cool.y中被使用. The
classconstructor returns an AST of type (or phylum)Class_. - 基本同上: cool-tree.h结尾处定义了在cool.y里用到的constructor, 实际上返回的是对应的class构造函数. 比如
class__class()method_class()等等.
- 在aps文件中定义的constructor在cool.y中被使用. The
- 真的是太多了. 哪里看的过来.
a terminal (
CLASS), a non-terminal (class), a constructor (class_), and a phylum (Class_).1
2
3typedef Class__class *Class_;
Class_ class__class::copy_Class_(){
return new class__class(copy_Symbol(name), copy_Symbol(parent), features->copy_list(), copy_Symbol(filename)); }反正bison只管推导, 至于分析出结果之后用什么结构存储管理就是我们在定义的部分和其他文件里所写的那样.
如果要看更多可能要分析bison的输出文件, 暂时不看了. 接下来是语义分析.
3.semantic - 语义分析
- Look at all classes and build an inheritance graph.
- Check that the graph is well-formed.
- For each class
(a) Traverse the AST, gathering all visible declarations in a symbol table.
(b) Check each expression for type correctness.
(c) Annotate the AST with types.
- semant.h结构如下
- 注意到symboltable中有三个typedef, 其中SymtabEntry里存储了id和info.
tbl指向当前的最里面一层的scope, 当然他是一个list, 可以通过tl()继续找到上一层scope的list节点. - InheritanceNode就是在class_class的基础之上添加了父子类的指针, 还有reachability basic_status+env这些信息. 因为很明显需要存储该类的所有子类以便于继承树检查.
- 而ClassTable以InheritanceNode的形式存储了所有的class, 文件中所有class检查完之后进入ClassTable的构造函数, 调用private functions例如install_class, build_inheritance_tree等来分析判断继承树的合法性.
- 创建这三个class的目的也很明显, 语法分析得到的无语法错误的AST树节点由
Program_class一类class组成, 但是节点能够存储的信息不够用于继承树和类型检查, 所以在class的基础上添加一些信息继承出InheritanceNode, 再由ClassTable管理, 最终所有的method class var都由一个最大的Environment class管理.
classDiagram
class InheritanceNode
class ClassTable{
-List<InheritanceNode> *nds
-install_class()
-check_improper_inheritance()
-build_inheritance_tree()
some_other_funcs()
}
class SymbolTable~Symbol, InheritanceNode~{
typedef SymtabEntry<SYM,DAT> ScopeEntry;
typedef List<ScopeEntry> Scope;
typedef List<Scope> ScopeList;
-ScopeList *tbl;
+enterscope() void
+exitscope() void
+addid() ScopeEntry*
+lookup() DAT*
+probe() DAT*
+dump() void
}
InheritanceNode <|-- class__class : Inheritance
ClassTable <|-- SymbolTable~Symbol, InheritanceNode~ : Inheritance
class Environment{
-SymbolTable~Symbol, method_class~ method_table;
-SymbolTable~Symbol, Entry~ var_table;
-ClassTableP class_table;
-Class_ self_class;
method表操作函数
variable表操作函数
type操作函数get_self_type等等
}
InheritanceNode : 该class的信息和environment
class SymtabEntry {
-SYM id; // the key field
-DAT *info; // associated information for the symbol
+get_id() SYM
+get_info() DAT *
}
SymbolTable~Symbol, InheritanceNode~ <|-- SymtabEntry : Inheritance
要我写这些东西只能一点点加成员函数啥的, 现在勉强理清楚了结构感觉也能体会到怎么想出这样的程序逻辑.
先看semant-parse.cc入口main函数
1 | |
先是handle_flags()这不知道要干嘛的函数, 然后是ast_yyparse()构造好AST然后将根节点赋值给ast_root, 再执行program_class的semant()函数, dump_with_types()输出AST(不知道要怎么看, 算了也不重要)
再看semant()函数:
1 | |
可以想到在ClassTable的构造函数中完成检查AST树, 其中一个流程如下:
This file implements the semantic checks for Cool. There are three passes:
- Pass 1: This is not a true pass, as only the classes are inspected. The inheritance graph is built and checked for errors. There are two “sub”-passes: check that classes are not redefined and inherit only from defined classes, and check for cycles in the inheritance graph. Compilation is halted if an error is detected between the sub-passes.
- enterscope : 新建一个tbl
- install_basic_classes : 注意有三个不可继承的class(No_class SELF_TYPE prim_slot), 具体见semant.cc
- install_classes : 装载构造函数的参数classes
- check_improper_inheritance :
- build_inheritance_tree
- root()->mark_reachable()
- check_for_cycles
- Pass 2: Symbol tables are built for each class. This step is done separately because methods and attributes have global scope—therefore, bindings for all methods and attributes must be known before type checking can be done.
- build_feature_tables : 现在有了继承树,
- 首先是初始化Object的env和build_feature_tables(),
- 再向env的meth_table或var_table加入该feature, 这个过程中顺带检查一下是否重复定义, 是否错误重载(针对method), 当前类和祖先类是否重名变量(针对attr)
- 然后copy the parent’s environment to children’s env, 继续递归迭代.
- check_main : 这个是检查main class和main method是否存在以及main method参数不能为0.
- build_feature_tables : 现在有了继承树,
- Pass 3: The inheritance graph—which is known to be a tree if there are no cycles—is traversed again, starting from the root class Object. For each class, each attribute and method is typechecked. Simultaneously, identifiers are checked for correct definition/use and for multiple definitions. An invariant is maintained that all parents of a class are checked before a class is checked.
- root()->type_check_features : 有个东西是type的比较. method最后一条语句的type要<=return_type. 具体见kp博客和代码
相应的构造函数为:
1 | |
然后各种细节细到难以置信, 都不敢想象我自己写到底要用掉多少时间
再次回头看感觉没有那么复杂了. 希望到时中间代码优化也是如此.
What requirements do I need to check?
When do I need to check a requirement?
When is the information needed to check a requirement generated?
Where is the information I need to check a requirement?
4.codeGenerate - 代码生成
这部分的代码更长了, 诶可真累, 真实的要求可是自己写.
- Determine and emit code for global constants, such as prototype objects.
- Determine and emit code for global tables, such as the class nameTab, the class objTab, and the
dispatch tables. - Determine and emit code for the initialization method of each class.
- Determine and emit code for each method definition
拜拜了, 看累了跳过.
代码生成框架:
1 | |
- 在生成目标代码前,需要先读入AST的相关信息,**重建继承图[1],并自上而下的初始化相关的映射表格
在该初始化过程中,每个类会遍历其中的feature,并将其相关信息添加至对应的SymbolTable中
如果该feature是method,则还会额外自顶向下计算所需要的最小临时变量数量[2]**,并将其添加进表格中。
- init()的过程:
- 从形参中得到该class初始feature个数
- assign_tag
- 各种enterscope
- 装载features, 用到了layout_featues:
- layout_method():
- layout_attr():
- 各种map的赋值
- code()的过程:
1 | |
声明全局变量。例如以下mips汇编代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19.data
.align 2
.globl class_nameTab
.globl Main_protObj
.globl Int_protObj
.globl String_protObj
.globl bool_const0
.globl bool_const1
.globl _int_tag
.globl _bool_tag
.globl _string_tag
_int_tag:
.word 3
_bool_tag:
.word 4
_string_tag:
.word 5
.globl _MemMgr_INITIALIZER声明GC器。例如以下汇编代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9_MemMgr_INITIALIZER:
.word _NoGC_Init
.globl _MemMgr_COLLECTOR
_MemMgr_COLLECTOR:
.word _NoGC_Collect
.globl _MemMgr_TEST
_MemMgr_TEST:
.word 0
.word -1将常量输出(例如:数字,字符串,布尔常量),例如以下部分汇编代码
数字常量包括
0,字符串常量包括空字符串""1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9.word -1 # eye catcher for _gc_check
str_const8: # 该字符串的标签
.word 5 # string class tag
.word 6 # size of the class(include 5,6,string_disptab,string and align)/word
.word String_dispTab # 该类型可以使用的方法
.word int_const2 # 字符串长度(其中的int_const2指向另一个数字常量)
.ascii "Main" # 字符串的ASCII码
.byte 0 # 字符串末尾的\0终结符
.align 2 # 对齐将所有类的名称输出。例如以下汇编代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7class_nameTab: # 这一个个的str_const都指向特定的字符串
.word str_const6 # str_const6 => "Object"
.word str_const7 # str_const7 => "IO"
.word str_const8 # str_const8 => "Main"
.word str_const9 # str_const9 => "Int"
.word str_const10 # str_const10 => "Bool"
.word str_const11 # str_const11 => "String"将所有类中的object table输出(未知用途,删除后仍然可以执行)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13class_objTab:
.word Object_protObj
.word Object_init
.word IO_protObj
.word IO_init
.word Main_protObj
.word Main_init
.word Int_protObj
.word Int_init
.word Bool_protObj
.word Bool_init
.word String_protObj
.word String_init将每个类所含的方法输出(包括该类的继承类中的方法),例如以下汇编代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9Main_dispTab:
.word Object.abort
.word Object.type_name
.word Object.copy
.word IO.out_string
.word IO.out_int
.word IO.in_string
.word IO.in_int
.word Main.main将每个类的类型信息输出。
protObj中含有当前类的属性以及函数表。例如以下部分汇编代码1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9.word -1 # -1 header for the garbage collector(eye catcher for _gc_check)
Main_protObj: # label
.word 2 # class tag
.word 7 # total_attributes + DEFAULT_OBJFIELDS
.word Main_dispTab # 函数表
.word int_const0 # 第一个attribute是数字类型
.word str_const12 # 第二个attribute是字符串类型
.word bool_const0 # 第三个attribute是布尔类型
.word 0 # 第四个attribute是其他类型,例如各种类声明全局代码段的相关信息,例如以下汇编代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11#声明堆的相关信息
.globl heap_start
heap_start:
.word 0
#声明text代码段
.text
.globl Main_init
.globl Int_init
.globl String_init
.globl Bool_init
.globl Main.main输出每个类的初始化函数的代码,例如以下汇编代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14String_init:
addiu $sp $sp -12
sw $fp 12($sp)
sw $s0 8($sp)
sw $ra 4($sp)
addiu $fp $sp 4
move $s0 $a0
jal Object_init
move $a0 $s0
lw $fp 12($sp)
lw $s0 8($sp)
lw $ra 4($sp)
addiu $sp $sp 12
jr $ra